Disaster management
Source: Department of Planning, Uttar Pradesh (as Per Annual Plan 2014-15)
Hazard & Vulnerability Profile of U.P.
Uttar Pradesh is the largest state of the country having 18 administrative divisions consisting of 75 districts.
Uttar Pradesh, with 199.5 million people is the most populous state in India. The growth rate of the population of Uttar Pradesh is about 20% per decade which is alarmingly high growth rate in the country.
The Per Capita Income of India is Rs. 60972 whereas in U.P. it is Rs. 29417 per year. With second lowest Per Capita Income in the country, Uttar Pradesh is one of the poorest & most multi hazard prone state.
Natural disasters that are of significance in Uttar Pradesh are – Floods, Droughts, Fires and Earthquakes. Loss of life and property from these disasters, especially the former three, are in terms of hundreds of crores of rupees annually.
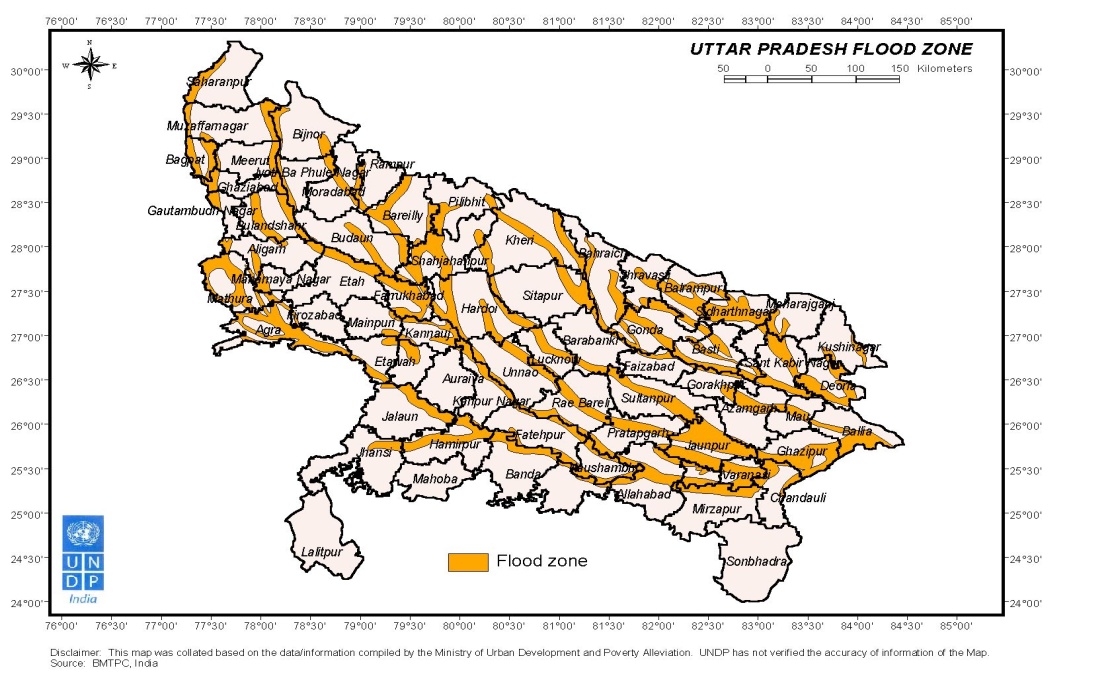 UP is vulnerable from the aspect of man made hazards too i.e. stampede, chemical, radiological and other hazards.
UP is vulnerable from the aspect of man made hazards too i.e. stampede, chemical, radiological and other hazards.
Flood
Eastern part of the state is traditionally flood prone but since last few years western Uttar Pradesh has also experienced massive flood situation. Approx 7.34 million hectare area gets affected annually due to Floods. Annual approx. loss due to floods is Rs. 432 crores.
Number of human loss due to floods & thunder storm is 380 in the year 2013.
Drought
 Drought is another major disaster affecting Uttar Pradesh. The State has been divided into two meteorological sub-divisions, viz. U.P. East, and U.P. West.
Drought is another major disaster affecting Uttar Pradesh. The State has been divided into two meteorological sub-divisions, viz. U.P. East, and U.P. West.
The recurrence of highly deficient rainfall in East U.P. occurs approximately every 6 to 8 years whereas in West U.P. it is 10 years.
The loss due to drought in the State depends upon the severity of the drought.
In the recent past, the year 2002, 2004 and 2009 have been severe in terms of drought, with losses to crop, livestock and property amounting to Rs.7540 crores and Rs. 7292 crores respectively.
In 2009, 59 districts were declared drought affected.
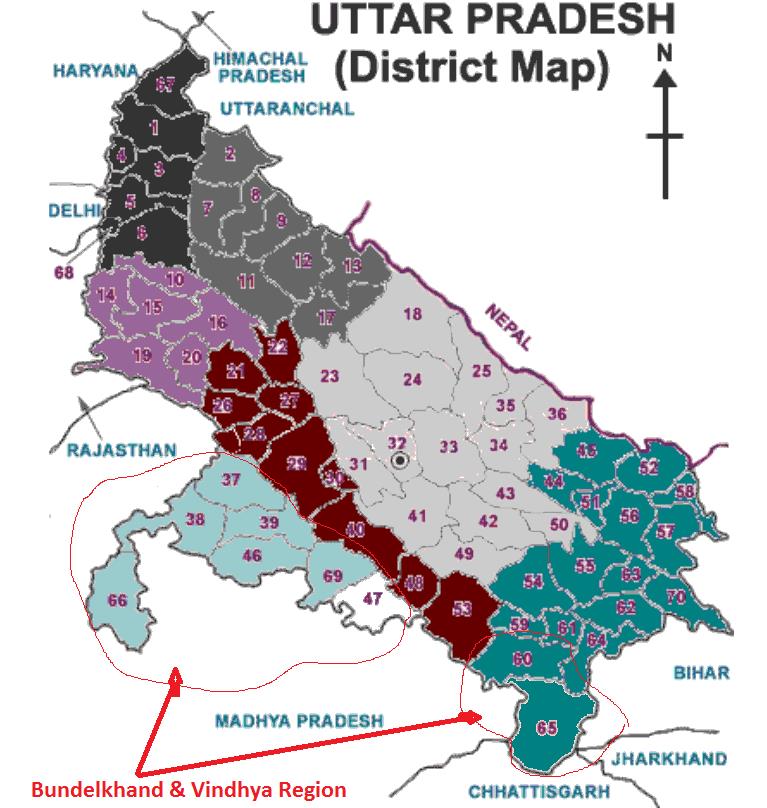
 Bundelkhand & Vindhya region of Uttar Pradesh is traditionally drought prone. Recurrent period of deficient rainfall is 3-4 years
Bundelkhand & Vindhya region of Uttar Pradesh is traditionally drought prone. Recurrent period of deficient rainfall is 3-4 years
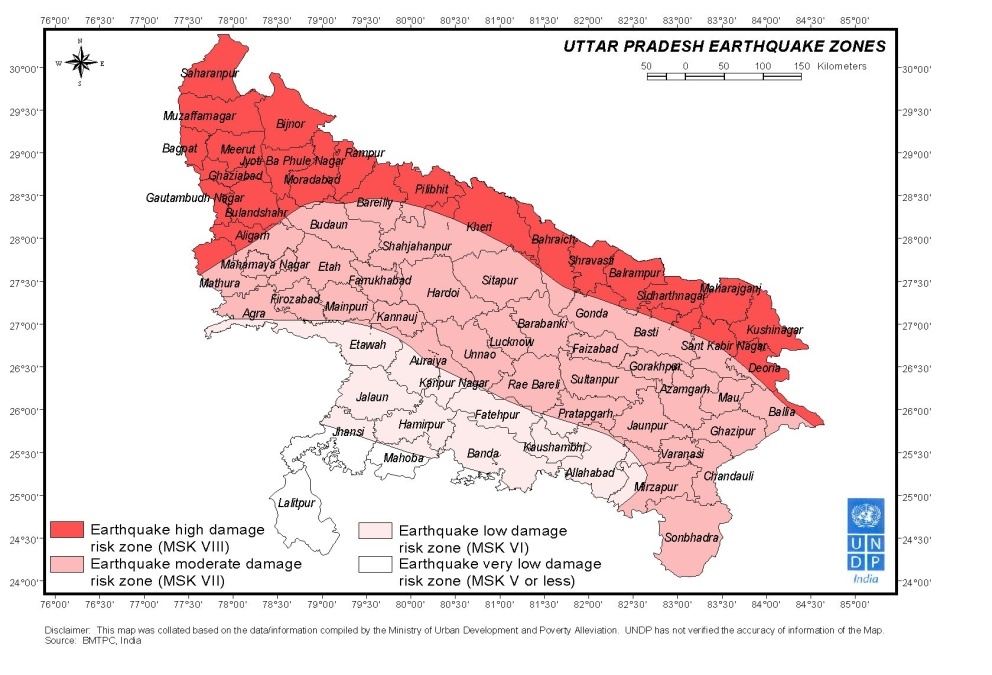
Earthquake
The Terai belt districts of UP and entire districts of Saharanpur, Muzaffarnagar, Bagpat, Bijnor, Meerut, Ghaziabad, Gautambuddh Nagar, JP Nagar, Rampur, Moradabad, Bulandshar, in western UP are in Earthquake High Damage Risk Zone-IV. 31 Districts of Uttar Pradesh are in Earthquake Risk Zone -III
Chemical & Industrial Hazard
There are 2,456 factories of hazardous nature in the state.
Nuclear Hazard
There is a atomic power plant in Narora, Bulandshahar district of Uttar Pradesh.
Fire Hazard
Due to large number of thatched houses, incidents of rural fire are very high.
Unorganized & unsystematic development has lead to increase in urban fire events.
Number of human loss due to fire events per year is average100.
Key Initiatives in the field of Disaster Management by Govt of Uttar Pradesh:-
Legal Mechanism:-
State DM Act, 2005 was passed even before the National Act.
State Fire Safety Act passed.
Financial Mechanism:-
Budget provision for SDMA & DDMA in state budget.
UP is one of the few states to have dedicated fund provision for resettlement/ rehabilitation of displaced due to floods.
Govt of UP has created State Disaster Mitigation Fund.
Institutional Development
UP State Disaster Management Authority set up in the year 2006. 1 Meeting of Governing Board of UPSDMA has taken place under the chairmanship of Hon’ble Chief Minister Members of the Governing Board of UPSDMA are:-
- Hon’ble Chief Minister - Chairperson
- Hon’ble Minister, Revenue - Vice Chairpeson
- Hon’ble Minister, Agriculture - Member
- Hon’ble Minister, Irrigation - Member
- Chief Secretary - Member
- Agriculture Production Commissioner- Member
- Principal Secretary, Revenue - Member
- Principal Secretary, Home - Member
- Principal Secretary, Finance - Member
Special Invitees:-
- Principal Secretary, Energy/ Urban Development/ Medical & Health/ Irrigation/ Agriculture/ Panchayati Raj/ Forest/ Environment
- DG Police
- Director Remote Sensing Application Center
Uttar Pradesh SDMA is accountable for various actions as envisaged in National DM Act i.e.-(As per Section 18 (2) of National DM Act, 2005)-
Without prejudice to the generality of provisions contained in subsection (1), the State Authority may-
- lay down the State disaster management policy;
- approve the State Plan in accordance with the guidelines laid down by the National Authority;
- approve the disaster management plans prepared by the departments of the Government of the State;
- lay down guidelines to be followed by the departments of the Government of the State for the purposes of integration of measures for prevention of disasters and mitigation in their development plans and projects and provide necessary technical assistance therefor;
- coordinate the implementation of the State Plan;
- recommend provision of funds for mitigation and preparedness measures;
- review the development plans of the different departments of the State and ensure that prevention and mitigation measures are integrated therein;
- review the measures being taken for mitigation, capacity building and preparedness by the departments of the Government of the State and issue such guidelines as may be necessary.
State Executive Committee constituted. SEC Meetings are regularly organized. Members of the Governing Board of UPSDMA are:-
- Chief Secretary - Chairperson
- Agriculture Production Commissioner - Member
- Principal Secretary, Home - Member
- Principal Secretary, Finance - Member
- Relief Commissioner - Member
Special Invitees:-
Principal Secretary/ Secretary of Revenue/ Energy/ Urban Development/ Medical & Health/ Irrigation/ Agriculture/ Panchayati Raj/ Forest/ Environment
DG Police
Director Remote Sensing Application Center
State Executive Committee of Uttar Pradesh SDMA is accountable for various actions as envisaged in National DM Act i.e.-(As per Section 22 (2) of National DM Act, 2005)- Without prejudice to the generality of provisions contained in subsection (1), the State Executive Committee may-
(a) coordinate and monitor the implementation of the National Policy, the National Plan and the State Plan;
(b) examine the vulnerability of different parts of the State to different forms of disasters and specify measures to be taken for their prevention or mitigation;
(c) lay down guidelines for preparation of disaster management plans by the departments of the Government of the State and the District Authorities;
(d) monitor the implementation of disaster management plans prepared by the departments of the Government of the State and District Authorities;
(e) monitor the implementation of the guidelines laid down by the State Authority for integrating of measures for prevention of disasters and mitigation by the departments in their development plans and projects;
(f) evaluate preparedness at all governmental or non-governmental levels to respond to any threatening disaster situation or disaster and give directions, where necessary, for enhancing such preparedness;
(g) coordinate response in the event of any threatening disaster situation or disaster;
(h) give directions to any Department of the Government of the State or any other authority or body in the State regarding actions to be taken in response to any threatening disaster situation or disaster;
(i) promote general education, awareness and community training in regard to the forms of disasters to which different parts of the State are vulnerable and the measures that may be taken by such community to prevent the disaster, mitigate and respond to such disaster;
(j) advise, assist and coordinate the activities of the Departments of the Government of the State, District Authorities, statutory bodies and other governmental and non-governmental organizations engaged in disaster management;
(k) provide necessary technical assistance or give advice to District Authorities and local authorities for carrying out their functions effectively;
(l) advise the State Government regarding all financial matters in relation to disaster management;
(m) examine the construction, in any local area in the State and, if it is of the opinion that the standards laid for such construction for the prevention of disaster is not being or has not been followed, may direct the District Authority or the local authority, as the case may be, to take such action as may be necessary to secure compliance of such standards;
(n) provide information to the National Authority relating to different aspects of disaster management;
(o) lay down, review and update State level response plans and guidelines and ensure that the district level plans are prepared, reviewed and updated;
(p) ensure that communication systems are in order and the disaster management drills are carried out periodically;
(q) perform such other functions as may be assigned to it by the State Authority or as it may consider necessary.
With the support of UNDP Human Resource, UPSDMA was made functional in the year 2010. There are 100 positions sanctioned in UPSDMA on deputation basis but due to lack of officers in other departments who are experienced on disaster management, no position could be filled up on deputation in UPSDMA. UNDP staff who was working previously with UPSDMA has been absorbed under 13th FC Capacity Building Programme to carry out functions at UPSDMA.
Uttar Pradesh State Disaster Management Institute (UPSDMI) is established in the year 2011. This institute has organized 89 trainings/ workshops/ seminar/ conferences and trained more than 6000 officers of various departments & other stakeholders on Disaster management. UPSDMI supported in development of Disaster Management Modules for various probation/ in-service training programmes in State i.e. PCS foundation, Medical Officer foundation, Teacher’s Training, etc. Various training manuals/ guidelines/ IEC material developed in Hindi and disseminated.
District Disaster Management Authority is constituted in all the districts. First time the budget was allocated & transferred to DDMAs in the year 2012-13 to carry out various activities as mandated in DM Act 2005.
Emergency Operation Center: Exclusive Emergency Operation Centres set up at State level & in 13 district headquarters viz – Badayun, Bahraich, Basti,Bijnor, Balrampur, Deoria, Gonda, Gazipur, Gorakhapur, Rampur, Siddharthnagar, Sitapur & Saharanpur. In other districts EOC is functional from collector’s office.
School Safety:- UP was the first state to initiate the earthquake safe school buildings. Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan (Govt of India) adopted UP success story & implemented earthquake safe school model in all other states. Integration of Disaster Management Curriculum has been done in state education board curriculum.
Techno-legal Regime:- Amendment in building bylaws & codes has been done and these amendments have been Adopted & Implemented by all the development authorities & departments.
Mainstreaming Disaster Risk Reduction (DRR) into Development:- A committee was setup under the chairmanship of Principal Secretary Planning fro DRR Mainstreaming. A study on “Entry points for DRR Mainstreaming in development” was conducted in the year 2013-14. A GO on “DRR Mainstreaming in development” has been issued by Chief Secretary on the basis of above study. The departments where mainstreaming initiatives are being carried out are:-
- Planning
- Health
- Fire
- Civil Defence
- Rural Development
- Education
- Panchayati Raj
- PAC
- State Institute of Health & Family Welfare
- SIRD
- ATI
State Disaster Management Plan prepared and shared with NDMA & various departments at the state level.
District Disaster Management Plans are being prepared in each district.
18 Hazard specific plans prepared.
|
Floods
|
Biological Attacks
|
|
Dam Burst
|
Radiations
|
|
Earthquakes
|
Drought
|
|
Storms
|
Serial Bombing & Explosions
|
|
Human
|
Communal Riots
|
|
Livestock/Avian Species
|
Civil Disobedience & Mass Agitation
|
|
Pest Attack
|
Nuclear Attacks
|
|
Biological
|
Chemical Attacks
|
|
Chemical Leakage/ Spillage
|
Gas Leakage & Explosions
|
SOPs for 14 Emergency Support Functions are prepared:-
|
1
|
Media
|
|
2
|
Donation
|
|
3
|
Public Works & Engineering
|
|
4
|
Food
|
|
5
|
Information & Planning
|
|
6
|
Drinking Water
|
|
7
|
Transport
|
|
8
|
Public Health & Sanitation
|
|
9
|
Shelter
|
|
10
|
Communications
|
|
11
|
Relief Supplies
|
|
12
|
Helplines
|
|
13
|
Power
|
|
14
|
Search & Rescue
|
Special Programmes going on in UP SDMA/ Relief Commissioner Organisation:
13th FC Capacity Building Grant:
Effective disaster response requires trained manpower to deal with complex situations where effective and speedy handling reduces the impact of a disaster on human life and property. Therefore it is necessary to continuously undertake measures to build capacity amongst those responsible for disaster response and augmenting public awareness. Accordingly, FC-XIII has recommended a grant of Rs. 25 crore for building capacity for better handling of disaster response and for preparation of district and state level disaster management plans This grant will be released in five equal annual installments from the year 2010 to 2015. In order to build the capacities of community which are at the forefront during disasters, State govt of Uttar Pradesh has planned a Community Based Disaster Risk Reduction Program to provide disaster management trainings & basic equipments upto grass root level i.e. Gram Panchayats under 13th Finance Commission Capacity Building Grant. Objective of the Capacity Building Programme which is being implementaed in the state are:-
The Community Based DRR process will lead to progressive improvements in public safety and community disaster resilience. It will contribute to equitable and sustainable community development in the long term.
Constitution & training of Disaster Management Teams at state, district and Gram Panchayat level.
Development of District Disaster Management Plan
Mainstreaming of Disaster Risk Reduction into development plans and schemes at various level
Approach & Methodology to implement the Programme
There will be three levels of trainings. The first level will be training of principal trainers at state level, Second would be training of trainers at district level and third level will be trainings at Gram Panchayat level.
The training programme is designed to increase awareness and coping capacity on disaster situation at district and Gram Panchayat level. It covers various steps of disaster management i.e. preparedness, mitigation, risk reduction, mainstreaming of DRR components into development plans, better management of disasters, epidemic control, shelter management, search & rescue methods, first aid, etc and the tools for risk reduction and management.
Various task forces also will be constituted at the Gram Panchayat level which will be given specialized trainings to deal with the disasters.
Implementation Plan At State Level
04 institutes i.e. State Disaster Management Institute, ATI, State Institute of Rural Development and Sahbhagi Shikshan Kendra have been identified as state level training institutes to provide ToTs at the state level. These institutes are already having the capacity and resources to impart trainings on Community Based Disaster Risk Reduction.
I
mplementation Plan At District Level:-
Resources & infrastructure of Regional Institute of Rural Development (RIRD), District Institute of Rural Development (DIRD), District Institute of Education & Training (DIET), NGO, Civil Defence set-up at district level are being used for conducting CBDM trainings. Trainers for district level trainings are being trained at state level. grass root level govt. functionaries i.e. Teacher, Lekhpal, VDO, ANM, Shiksha Mitra, ASHA, People of community/ PRI who have got training skills, etc are being given training at district level. These trained persons are further imparting training at GP Level.
Implementation Plan At Gram Panchayat Level:-
Resources & infrastructure of Gram Panchayat Bhawan, Gram Panchayat Sachivalaya, School, NGO etc are being utilized to conduct Gram Panchayat level trainings. grass root level govt. functionaries i.e. Teacher, Lekhpal, VDO, ANM, Shiksha Mitra, ASHA, PRI Members, People of community, SHGs, Yuvak Managal Dal, Mahila Managal Dal, PRD, NYK, etc are being given training at GP level. Trainers who are giving GP level trainings have been trained at district level.
National School Safety Programme:
With the support of National Disaster Management Authority, UPSDMA is implementing National School Safety Programme in two districts of Uttar Pradesh. These districts are Lakhimpur Khiri & Ghaziabad.
|
|
Activities
|
Rs. in lakh
|
|
1
|
Translation into regional language and Printing of Teachers Training Module
|
1.60
|
|
2
|
Training of Trainers
|
2.75
|
|
3
|
Training of Teachers
|
27.60
|
|
4
|
Review and approval of school DM plans
|
1.85
|
|
5
|
Disaster preparedness kits 200 schools in each of 43 districts
|
3.70
|
|
6
|
Mock drill in 200 schools in each of 43 districts
|
3.70
|
|
7
|
Translation, printing dissemination of IEC
|
1.80
|
|
8
|
Sensitization programme at State level
|
1.80
|
|
9
|
Grant in Aid to state education department for sensitization programme and awareness activities
|
23.00
|
|
10
|
Rapid Visual survey in 200 schools in each of 43 districts
|
22.00
|
|
11
|
Non-structural mitigation measures in 200 Schools in each of 43 districts
|
37.00
|
|
12
|
Structural Retrofitting of one school each 22 States/UTs
|
25.09306
|
|
|
Total
|
151.89306
|
|
|
|
|
Disaster Risk Reduction Programme:
Disaster Risk Reduction Programme has got approval of UNICEF. This programme is being implemented from the year 2013 till December 2017. Main objectives of this programme are:-
Study & Assessment of disaster management systems in the state (at State As well as district level) & the impacts of 13th FC capacity building program on ‘Disaster Risk Reduction (DRR)’
To support with the HR to Support UP Govt. in Institutional development as per National DM Act, National DM Policy & State Govt. needs.
Mainstreaming of Disaster Risk Reduction
Capacity development of stakeholders.
School & Children Safety.
Hospital safety
Strengthening of MIS to monitor DRR mainstreaming progress
Development of integrated action plan for Climate Change Adaptation and Disaster Risk Reduction.
IEC/ Manual/ Course Curriculum development/ Documentation/etc
Awareness & Sensitization
Community based Disaster Risk Reduction.
Robust MIS systems which will help in monitoring of the progress made in relation with DRR by various departments.
Community based scaleable models integrating CCA and DRR measures in different hazard prone areas & resilience development.
Urban Risk Reduction
Developing cadre of experts/master trainers for supporting the Capacity Building, Training & Education intiatives especially for response, mainstreaming DRR.
Strengthening of knowledge management, Information and Research Network
Disasters which have occurred in the year 2013-14:
Floods:
Recent onset of monsoons resulting in heavy rainfalls caused widespread flooding and water logging in 41 districts of Uttar Pradesh. The impact of floods got increased due to many inter-state rivers which got swollen as a result of heavy rainfall in adjoining states.
In June 2013, a multi-day cloudburst centered on Uttarakhand which caused devastating floods and landslides in the country's worst natural disaster. Heavy rains in Himachal Pradesh, Haryana, Delhi, Madhya Pradesh added more water to rivers which caused widespreading flooding.
U.P. is an important sub-system of the Ganga and drains about 127950 sq. km. area in India and Nepal and brings an average annual flow of 94,400 mill. c.m.(peak discharge 6,700 cumecs). Its upper catchments is hilly which lies in Nepal (average elevation 4000 m.) and accounts for about 75% of its total area. Its upper tributaries are snow-fed. The basin is highly conical in shape. The Ghaghra meets the Ganga near Chapra city.
This fury of the Nature has resulted in large-scale damages, not restricted only to the loss of crops and property but also to the loss of cattle and human life. The total numbers of affected villages are more than 1878 approx., involving about 42.86 lacs population. According to estimates about 15.41 lacs hectare sown agricultural area is adversely affected. This calamity has claimed the life of more than 344 people besides 469 cattle. About 76663 houses have also been damaged. It has also adversely affected the infrastructure facilities; such as roads, waterworks, irrigation channels, bunds, health facilities and buildings of educational institutions.
Extent of Damage:
|
Affected Districts (39)
Aligarh, Allahabad, Azamgarh, Amroha, Ballia, Basti, Banda, Bandaun, Barabanki, Bahraich, Bijnaur, Balrampur, Chandauli, Chitrkoot, Deoria Farukhabad, Faizabad, Gazipur, Gorakhpur, Gonda, Hamirpur, Jalaun, Kannauj, Hapud, Lakhimpur Khiri, Mirzapur, Muzaffar Nagar, Moradabad, Meerut, Pilibhit, Saharanpur, Sambhal, Sant Kabir Nagar, Siddarth Nagar, Sitapur, Shravasti, Shamli, Sambhal, Varanasi
|
|
Number of affected Tehsils
|
109
|
|
Number of affted Villages
|
5785
|
|
Population affected (in lacs)
|
35.44
|
|
Number of human lives lost
|
380
|
|
Flood
|
130
|
|
Heavy Rainfall
|
165
|
|
Others
|
85
|
|
Number of Cattle/livestock lost/perished
|
550
|
|
Marooned Villages
|
1904
|
|
Area affected (in lakh ha)
|
|
|
Cropped area affected (in lakh hr)
|
797.50
|
|
Estimated value of damaged crop (Rs. In lakh)
|
25770.22
|
|
Houses damaged :-
|
|
|
No. of houses damaged :-
|
79602
|
|
Fully damaged (pucca + kutcha)
|
9713
|
|
Partly damaged houses (pucca + kutcha)
|
69889
|
|
Estimated value of damage to houses (Rs. In lakh)
|
7358.74
|
|
Fully damaged
|
3790.82
|
|
Partly damaged houses (pucca + kutcha)
|
3567.92
|
|
Damaged Infrastructure
|
|
|
Estimated value of damage to Public Properties (in lakh)
|
292824.27
|
|
Estimated value of total damage (C+D+E)
|
325953.23
|
|
Rescue and Relief Operations
|
|
|
Number of persons evacuated
|
620931
|
|
Number of Boats deployed
|
3690
|
|
Number of Relief Camps
|
454
|
|
Number of persons accommodated in the relief camps
|
347066
|
|
Number of Cattle Relief Camps
|
257
|
|
Number of Cattle accommodated in the relief camps
|
49528
|
|
GR paid, if any specify the items and amount (Rs. In lakh)
|
2522.15
|
|
No. of Districts where PAC & military deployed
|
PAC deployed in 16 Districts & Military deployed in 2 Districts
|
|
No. of Districts where NDRF deployed
|
NDRF deployed in 7 Districts
|
Management of Flood at the apex level:-
In May 2013, Meeting of district collectors was organized where all other concern departments participated.
Flood preparedness was reviewed regularly at the apex level and detailed instructions were given on various aspects of preparedness & relief.
During the Floods, 24X7 control room was set up in the office of Relief Commissioner. The control room was manned round the clock.
Daily Flood Reports were generated. These reports generated by the control room, were reviewed at the apex level in the state government. Information was sent to government of India and above information was also released to the press.
Future Agenda:
Strengthening of Uttar Pradesh State Disaster Management Authority.
Strengthening of Uttar Pradesh State Disaster Management Institute.
Finalization of State Disaster management Plan.
Strengthening of Emergency Operation Centers at districts as well as at the state level.
Appropriate amendments in the legislative and regulatory instruments (state laws, master plans, development area plan rules, building regulations and bye-laws of local bodies)
Ensuring that Disaster Risk Reduction components are being mainstreamed in various department’s activities & projects..
Strengthening of the enforcement mechanisms at different levels.
Hazard map zonation to all major river catchments area in Uttar Pradesh.
Address: Uttar Pradesh State Disaster Management Authority, B-2 Block, PICUP Bhawan, Vibhuti Khand, Gomti Nagar, Lucknow
Web Link: www.rahatup.nic.in
Email: upsdma@gmail.com